Toothaches are a concern that can disrupt daily life with pain and sensitivity. They occur for various reasons, making it useful to understand their causes, symptoms, and preventive measures. By knowing more about toothaches, you can take steps to reduce your risk and seek help when needed.
What Is a Toothache?
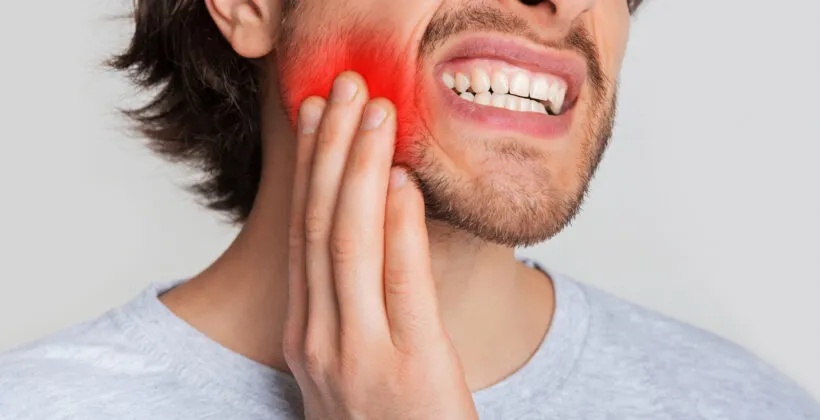
A toothache refers to pain or discomfort in or around a tooth. It can range from mild, intermittent sensitivity to a sharp or throbbing pain that persists for hours. Toothaches can also lead to symptoms such as swelling, tenderness, or sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures. These issues may indicate an underlying problem that requires attention.
What Causes Toothaches?
Toothaches may stem from several causes, both dental and non-dental in nature.
- Tooth Decay: Cavities caused by plaque and bacteria are a leading cause of toothaches. When decay penetrates the tooth enamel and reaches the dentin, it may trigger pain and sensitivity.
- Gum Disease: Also known as periodontal disease, this condition affects the gums and causes discomfort, bleeding, and swelling.
- Tooth Fractures: Chips or cracks in a tooth may expose the inner layers, leading to pain, particularly when eating or drinking.
- Abscesses: An infection near the root of a tooth or in the gums can result in severe pain and swelling.
- Grinding or Clenching: Habitual grinding or clenching of teeth (known as bruxism) may cause tooth and jaw pain over time.
- Non-Dental Causes: Sinus infections, ear problems, or nerve-related issues occasionally mimic tooth pain.
Identifying the specific cause often requires a dental evaluation to address the issue effectively.
How Is the Problem Diagnosed?
Diagnosing a toothache starts with a visit to an endodontist, who will conduct a thorough examination to identify the source of the pain. This evaluation typically includes a physical examination of your teeth and gums, using tools to check for sensitivity or discomfort, and possibly taking X-rays to detect issues like decay, fractures, or infections. A comprehensive diagnosis enables dental professionals to recommend the best course of treatment. By addressing the root cause of the problem efficiently, they can help relieve your pain and restore your oral health.
What Prevention Strategies Are There?
Preventing toothaches often involves maintaining good oral hygiene and adopting healthy habits. While no strategy guarantees immunity from dental issues, these steps may reduce the risk.
- Brush and Floss Regularly
- Limit Sugary Snacks and Drinks
- Visit the Dentist Regularly
- Wear a Mouthguard
- Address Symptoms Promptly
If you notice signs of sensitivity or discomfort, seeking early care may prevent minor issues from becoming more serious.
When Should You See an Endodontist?
An endodontist is a dental specialist focused on diagnosing and treating issues involving the tooth’s pulp and surrounding tissues. If you’re experiencing a toothache caused by deep decay, infection, or trauma to the pulp, an endodontist is often the best professional to provide relief and care. They are highly trained to handle treatments like root canals and other procedures that preserve the health of your teeth. You should visit an endodontist if your pain is severe and doesn’t improve with over-the-counter medication or if you notice symptoms like swelling or discharge, which may indicate an infection.
Learn More Today
Toothaches can be a sign of many underlying conditions, but understanding their causes and adopting preventive measures can make a difference in your oral health. If you’re experiencing tooth pain or have questions about prevention, contact a dental specialist for advice. A proactive approach helps your smile stay healthy and pain-free.